Class 10 Science Lesson 16 Note
#Unit -16 Gases
1. Choose the correct option for the following questions.
a) What products are formed on heating of limestone to a high temperature using coal?
i. Methane and lime
ii. Lime and carbon dioxide
iii. Acetylene and carbon dioxide
iv. Ammonia and lime
Answer: ii. Lime and carbon dioxide
b) Which of the following statements is true?
i. Carbon dioxide is collected in the gas jar by the upward displacement of air.
ii. Carbon dioxide is collected in the gas jar by the downward displacement of air.
iii. Carbon dioxide is collected in the gas jar by the upward displacement of water.
iv. Carbon dioxide is collected in the gas jar by the downward displacement of water.
Answer: ii. Carbon dioxide is collected in the gas jar by the downward displacement of air
c. Which compounds are formed when carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water for some time?
i. Calcium bisulphate
ii. Calcium bicarbonate
iii. Calcium sulphate
iv. Calcium carbonate
Answer: ii. Calcium bicarbonate
d. In what ratio should ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide be mixed for the laboratory preparation of ammonia gas?
i. 3:1
ii. 2:3
iii. 1:2
iv. 2:1
Answer: iii. 1:2
2. Give reason:
a) Carbon dioxide can be collected in an open glass jar.
Answer:
Because carbon dioxide is heavier than air, it does not escape easily when collected in an open jar. It displaces air and stays inside unless disturbed.
b) The bottle of liquid ammonia should be placed in cold water or ice for some time before opening its lid.
Answer:
Ammonia is a highly volatile gas with a low boiling point. If the bottle is not cooled, the gas will escape rapidly and may cause pressure buildup or frostbite. Cooling slows its evaporation, making it safer to open.
3. Answer the following questions:
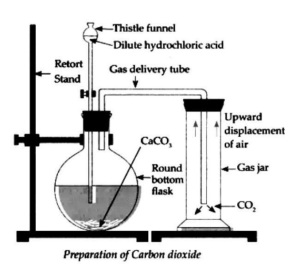
a. Describe the laboratory preparation of carbon dioxide with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Laboratory Preparation of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
1. Apparatus Required:
- Conical flask
- Thistle funnel
- Delivery tube
- Gas jar or test tube
- Beehive shelf
- Water trough
- Rubber cork with holes
- Stand and clamp
2. Chemicals Required:
- Dilute Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
- Calcium Carbonate (CaCO₃) – in the form of marble chips
3. Principle:
Carbon dioxide is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium carbonate (marble chips).
The chemical reaction is:
CaCO3+2HCl→CaCl2+H2O+CO2↑
4. Procedure:
- Take a clean conical flask and place some marble chips in it.
- Fix a thistle funnel and a delivery tube through a cork on the mouth of the flask.
- Ensure the stem of the thistle funnel dips into the acid.
- Pour dilute hydrochloric acid slowly through the funnel.
- The reaction between CaCO₃ and HCl starts producing CO₂ gas.
- The gas escapes through the delivery tube and is collected in an inverted gas jar over water using the downward displacement of water (or downward delivery if using air).
5. Test for Carbon Dioxide:
- Pass the collected gas through lime water (Ca(OH)₂ solution).
- If the lime water turns milky, it confirms the presence of carbon dioxide.
Ca(OH)2+CO2→CaCO3↓+H2O
6. Precautions:
- Handle hydrochloric acid with care; it is corrosive.
- Ensure the apparatus is airtight to avoid gas leakage.
- Do not use too much acid to prevent vigorous reaction.
b) Study the given figure and answer the following questions:
i. Which gas is being collected in the gas jar?
Answer: Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
ii. Write a balanced chemical reaction for the preparation of this gas.
Answer: CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂↑
iii. Which litmus paper is used to identify the gas?
Answer: Moist blue litmus paper — it turns red in carbon dioxide due to its acidic nature.
iv. Why is this gas collected in the gas jar kept straight upright?
Answer: Because carbon dioxide is heavier than air, it is collected by downward displacement of air. The upright position helps the gas settle in the jar.
c) Write any three properties of carbon dioxide gas.
Answer:
- It is colorless and odorless.
- It is heavier than air.
- It turns lime water milky by forming calcium carbonate.
d) Write any four uses of carbon dioxide gas.
Answer:
- Used in fire extinguishers.
- Used in the carbonation of soft drinks.
- Used in photosynthesis by plants.
- Used in cold storage as dry ice (solid CO₂).
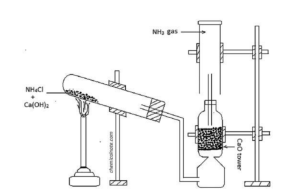
e. Describe the laboratory preparation of ammonia gas with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Laboratory Preparation of Ammonia Gas (NH₃)
1. Apparatus Required:
- Round-bottom or boiling tube
- Delivery tube
- Stand and clamps
- Thistle funnel
- Gas jar
- Water trough
- Rubber cork with holes
- Heat source (Bunsen burner)
2. Chemicals Required:
- Ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) – solid
- Slaked lime (Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂) – solid
3. Principle:
Ammonia gas is prepared by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and slaked lime.
The chemical reaction is:
2NH4Cl+Ca(OH)2→2NH3↑+CaCl2+2H2O
Ammonia is a colorless gas with a pungent smell and is lighter than air, so it is collected by the downward displacement of air.
4. Procedure:
- Mix dry ammonium chloride and dry slaked lime in a ratio of 2:1.
- Place the mixture in a dry round-bottom flask or hard glass test tube.
- Insert a thistle funnel and delivery tube through a cork.
- Heat the mixture gently using a Bunsen burner.
- Ammonia gas is evolved and passes through the delivery tube into an inverted dry gas jar.
- Collect ammonia by downward displacement of air (since it’s lighter than air and very soluble in water).
5. Test for Ammonia Gas:
- Smell: Sharp, pungent odor.
- Litmus Test: Turns red litmus paper blue (alkaline nature).
- Hydrogen chloride test: A glass rod dipped in concentrated HCl produces dense white fumes of ammonium chloride:
NH3+HCl→NH4Cl
6. Precautions:
- Use dry apparatus only. Ammonia is highly soluble in water and may dissolve if moisture is present.
- Do not collect over water.
- Handle ammonia gas in a well-ventilated area due to its pungent odor and potential irritation.
- Avoid excessive heating to prevent breaking the glassware.
f. Study the given figure and answer the following questions:
i. Which gas is being collected in the gas jar?
Answer: Ammonia (NH₃) gas.
ii. Write the balanced chemical equation for the preparation of this gas.
Answer: 2NH₄Cl + Ca(OH)₂ → 2NH₃ + CaCl₂ + 2H₂O
iii. Which litmus is used to identify this gas?
Answer: Moist red litmus paper — it turns blue, indicating ammonia is basic.
iv. Why the hard glass test tube is slightly inclined?
Answer: To prevent water droplets or reactants from flowing backward and cracking the hot test tube.
v. What is the use of the lime tower?
Answer: To dry the ammonia gas by passing it through quicklime (CaO), which absorbs moisture.
g. Write any four uses of ammonia gas.
Answer:
- Used in the production of fertilizers (like urea, ammonium nitrate).
- Used as a refrigerant gas in old cooling systems.
- Used in cleaning agents (window cleaners).
- Used in the manufacture of nitric acid via the Ostwald process.
h. What happens in the following processes? Write with a balanced chemical reaction.
i) Carbon dioxide is passed through lime water for some time.
Answer: Lime water turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
Balanced Reaction: Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ ↓ + H₂O
ii) Carbon dioxide is passed through lime water for a long time.
Answer: The milkiness disappears due to the formation of soluble calcium bicarbonate.
Balanced Reaction: CaCO₃ + CO₂ + H₂O → Ca(HCO₃)₂
iii) A burning magnesium ribbon is inserted into a jar full of carbon dioxide gas.
Answer: Magnesium continues to burn, forming magnesium oxide and carbon.
Balanced Reaction: 2Mg + CO₂ → 2MgO + C
iv) The mixture of ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide is heated.
Answer: Ammonia gas is produced.
Balanced Reaction: 2NH₄Cl + Ca(OH)₂ → 2NH₃ + CaCl₂ + 2H₂O
v) Ammonia is mixed with water.
Answer: Ammonia dissolves in water to form ammonium hydroxide, making the solution alkaline.
Balanced Reaction: NH₃ + H₂O ⇌ NH₄⁺ + OH⁻
vi) Ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Answer: Ammonium chloride is formed as white fumes or solid.
Balanced Reaction: NH₃ + HCl → NH₄Cl


